Inversion: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
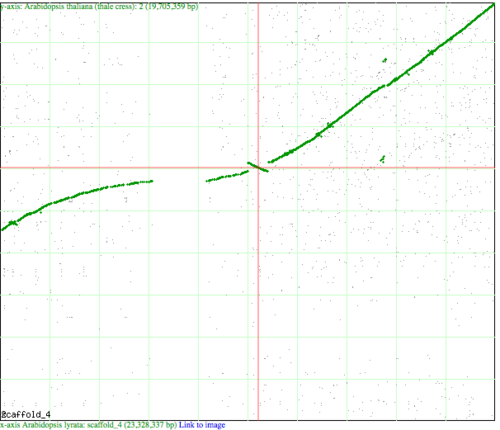
[[Image: | [[Image:SynMap-inversion.png|thumbnail|right|500 px|[[Syntenic dotplot]] visualized by [[SynMap]] between chromosome 4 of Arabidopsis lyrata (x-axis) and chromosome 2 of Arabidopsis thaliana (y-axis). Green dots represent syntenic genes as identified by DAGChainer. Note the inversion at the center of the cross hairs where the green "line" changes slope from positive to negative.]] | ||
[[ | |||
[[Image:GEvo-inversion.png|thumbnail|right|500 px|GEvo analysis of the inversion detected between the two Arabidopsis chromosomes. Results can be regenerated at http://toxic.berkeley.edu/CoGe/GEvo.pl?prog=blastz;spike_len=0;accn1=fgenesh2_kg.4__765__AT2G28060.1;fid1=30750039;dsid1=39129;dsgid1=3068;gstid1=1;chr1=scaffold_4;dr1up=830865;dr1down=1073591;gbstart1=1;gblength1=2332;mask1=non-cds;do1=1;accn2=AT2G28060;fid2=20219657;dsid2=35172;dsgid2=8;gstid2=1;chr2=2;dr2up=334450;dr2down=533528;gbstart2=1;gblength2=1591;mask2=non-cds;do2=2;num_seqs=2;hsp_overlap_limit=0;hsp_size_limit=0 ]] | |||
[[Image:1911 1906.CDS-CDS.blastn.dag geneorder D20 g10 A5.1-1.w800.png|thumb|right|500px|Syntenic dotplot generated by [[SynMap]] between two strains of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis showing one inversion. [http://synteny.cnr.berkeley.edu/CoGe/OrganismView.pl?dsgid=1911 Strain IP 31758] (x-axis); [http://synteny.cnr.berkeley.edu/CoGe/OrganismView.pl?dsgid=1906 strain YPIII] (y-axis). Results can be regenerated at: http://synteny.cnr.berkeley.edu/CoGe/SynMap.pl?dsgid1=1911;dsgid2=1906;D=20;g=10;A=5;w=0;b=1;ft1=1;ft2=1;dt=geneorder]] | |||
[[Image:Yersinia pseudotuberculosis-inversion-GEvo.png|thumb|right|500px|[[GEvo]] analysis of inversion breakpoints identified in two strains of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. At the breakpoints are ribosomal gene cassettes (shown as gray and yellow arrows). Results can be regenerated at: http://tinyurl.com/yj38xw6]] | |||
===Definition=== | |||
A genomic inversion is when a region of a genome or chromosome gets flipped in place. The orientation of this genomic segment changes such that its 5' and 3' ends change places. These usually happen at genomic regions with nearly identical sequence, implying a mechanism similar to [[non-homologous recombination]]. | |||
===Bacteria=== | |||
In bacterial genomes, inversion often occur at transposon or ribosomal gene sequences, and happen symmetrically around the [[origin of replication]]. The latter causes a characteristic pattern in [[syntenic dotplots]] called an [[x alignment]]. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:40, 18 February 2010



Definition
A genomic inversion is when a region of a genome or chromosome gets flipped in place. The orientation of this genomic segment changes such that its 5' and 3' ends change places. These usually happen at genomic regions with nearly identical sequence, implying a mechanism similar to non-homologous recombination.
Bacteria
In bacterial genomes, inversion often occur at transposon or ribosomal gene sequences, and happen symmetrically around the origin of replication. The latter causes a characteristic pattern in syntenic dotplots called an x alignment.