Deletion: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
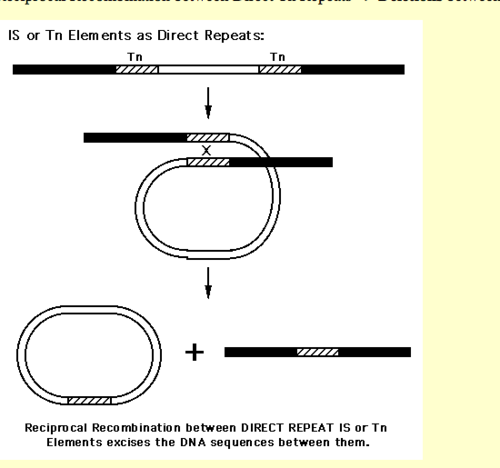
Deletion of a DNA segment can happen if it is bordered by direct repeats. These repeats can be introduced by insertion of same transposons in identical orientation. DNA will fold back in a closed loop structure with direct repeats positioned in a way two homologous chromosomes aligned in metaphase. This structure of DNA allows recombination to happen between two repeats resulting in a deletion of one repeat region and genes within the direct repeats. | Deletion of a DNA segment can happen if it is bordered by direct repeats. These repeats can be introduced by insertion of same transposons in identical orientation. DNA will fold back in a closed loop structure with direct repeats positioned in a way two homologous chromosomes aligned in metaphase. This structure of DNA allows recombination to happen between two repeats resulting in a deletion of one repeat region and genes within the direct repeats. | ||
[[Image:deletion.png|thumb|500px|center| Image taken from[http://www.biology.ucsd.edu/classes/old.web.classes/bimm100 | [[Image:deletion.png|thumb|500px|center| Image taken from[http://www.biology.ucsd.edu/classes/old.web.classes/bimm100.FA00/09.MobileElements.html#B] ]] | ||
Latest revision as of 23:28, 12 November 2009
Deletion of a DNA segment can happen if it is bordered by direct repeats. These repeats can be introduced by insertion of same transposons in identical orientation. DNA will fold back in a closed loop structure with direct repeats positioned in a way two homologous chromosomes aligned in metaphase. This structure of DNA allows recombination to happen between two repeats resulting in a deletion of one repeat region and genes within the direct repeats.