GC content shift: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
GC content shift is an evolutionary genome-wide change in the GC content of an organism. The evolutionary consequences of such a | GC content shift is an evolutionary genome-wide change in the GC content of an organism. The evolutionary consequences of such a shift results in a chance in codon and amino acid usage. The selective pressures driving GC content shifts are unknown. They are detected by comparing the genomes of two related organisms that share a recent common ancestor, and determining if their have different: | ||
*AT/GC genomic composition | *AT/GC genomic composition | ||
*High rate of synonymous mutations for [[syntenic gene pairs]] | *High rate of synonymous mutations for [[syntenic gene pairs]] | ||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces fungi japonicus strain yFS275 and pombe 972h-== | ==Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces fungi japonicus strain yFS275 and pombe 972h-== | ||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center; | *Schizosaccharomyces pombe: model laboratory organism. Originally isolated from east African millet beer in 1893. | ||
*Schizosaccharomyces japonicus: originally islated from strawberries near Kyusyu University, Japan in 1928. | |||
{| class="wikitable" style="text-align: center;" border="1" | |||
|+ Genome Overview | |+ Genome Overview | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 14: | Line 17: | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Length | ! scope="row" | Length | ||
| | | 11,300,431 || 10,082,004 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | GC% | ! scope="row" | GC% | ||
| | | 42.6 || 36 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | AT% | ! scope="row" | AT% | ||
| | | 54.9 || 64 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | CDS GC% | ! scope="row" | CDS GC% | ||
| | | 45.5 || 39.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | CDS AT% | ! scope="row" | CDS AT% | ||
| 5 || 60.5 | | 54.5 || 60.5 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Wobble GC% | ! scope="row" | Wobble GC% | ||
| | | 44.1 || 32.8 | ||
|- | |- | ||
! scope="row" | Wobble AT% | ! scope="row" | Wobble AT% | ||
| | | 55.9 || 67.2 | ||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | Codon Usage Table | |||
| [[Image:Schizosaccharomyces japonicus strain yFS275 codon usage table.png|thumb|center|300px]] || [[Image:Schizosaccharomyces pombe 972h codon usage table.png|thumb|center|300px]] | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | Codon Usage Table | |||
| [[Image:Schizosaccharomyces japonicus strain yFS275 amino acid usage table.png|thumb|center|100px]] || [[Image:Schizosaccharomyces pombe 972h amino acid usage table.png|thumb|center|100px]] | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | Histogram of [[CDS]] GC content | |||
| [[Image:41589 min CDS gc.png|thumb|center|300px]] || [[Image:5251 5249 min CDS gc.png|thumb|center|300px]] | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | Histogram of [[CDS]] [[wobble position]] GC content | |||
| [[Image:41589 wobble gc.png|thumb|center|300px]] || [[Image:5251 5249 wobble gc.png|thumb|center|300px]] | |||
|- | |||
! scope="row" | Histogram of [[CDS]] GC content - [[wobble position]] GC content | |||
| [[Image:41589 wobble gc diff.png|thumb|center|300px]] || [[Image:5251 5249 wobble gc diff.png|thumb|center|300px]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
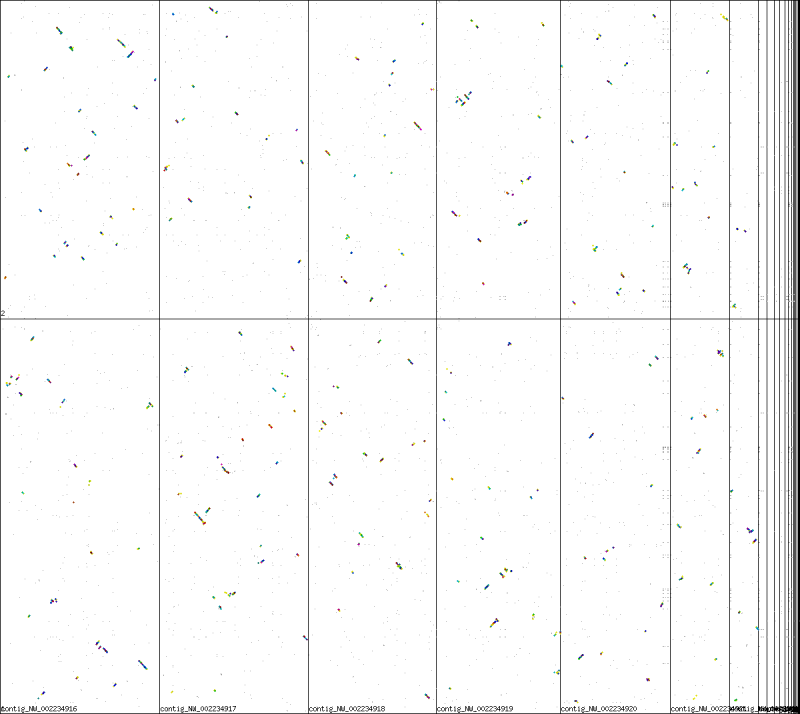
[[Image:Master 7763 1483.CDS-CDS.lastz.dag.go c4 D20 g10 A5.aligncoords.gcoords ct0.w1200.ks.png|thumb| | [[Image:Master 7763 1483.CDS-CDS.lastz.dag.go c4 D20 g10 A5.aligncoords.gcoords ct0.w1200.ks.png|thumb|center|800px|SynMap syntenic dotplot of two Schizosaccharomyces fungi: japonicus strain yFS275 (x-axis) and pombe 972h (y-axis). Syntenic gene pairs are colored based on their synonymous mutation rates (see histogram below). While there have been many genomic rearrangements since these lineages diverged, nearly every genomic regions in both species have a syntenic partner region (albeit it small regions of contiguous synteny). Results may be regenerated at: http://genomevolution.org/r/pi4]] | ||
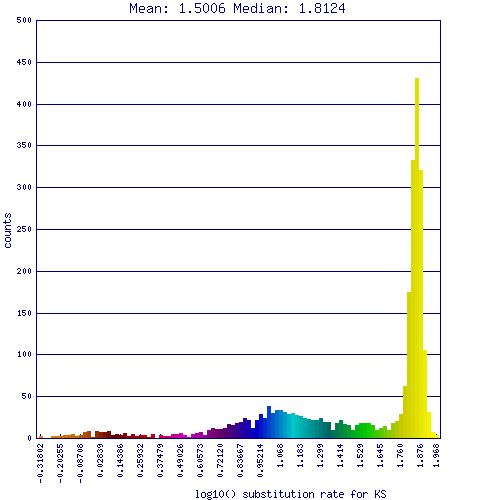
[[Image:Master 7763 1483.CDS-CDS.lastz.dag.go c4 D20 g10 A5.aligncoords.gcoords ct0.w1200.ks.hist.png|thumb| | [[Image:Master 7763 1483.CDS-CDS.lastz.dag.go c4 D20 g10 A5.aligncoords.gcoords ct0.w1200.ks.hist.png|thumb|center|500px|Histogram of synonymous mutation rates (Ks) for syntenic gene pairs identified between the Schizosaccharomyces fungi: japonicus strain yFS275 and pombe 972h. The Ks values have been log transformed. The yellow peak on the right (log(10) Ks ~ 1.8) is usually considered to be noise as they reflect an estimate of 60 changes per synonymous position. This many changes is beyond the saturation limits of the method used to estimate Ks (CodeML). This peak is the result of a GC content shift in one or both of these genomes since their divergence from a common ancestor. Results may be regenerated at http://genomevolution.org/r/pi4]] | ||
[[Image:GEvo-Schizosaccharomyces.png|thumb| | [[Image:GEvo-Schizosaccharomyces.png|thumb|center|800px|GEvo analysis of syntenic regions from the Schizosaccharomyces fungi japonicus strain yFS275 (top) and pombe 972h- (bottom). Gene models are colored based on the percent GC content of GC3. Red is AT rich; green GC rich; yellow 50/50 AT/GC. Results may be regenerated at: http://genomevolution.org/r/pi7]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:40, 26 August 2010
GC content shift is an evolutionary genome-wide change in the GC content of an organism. The evolutionary consequences of such a shift results in a chance in codon and amino acid usage. The selective pressures driving GC content shifts are unknown. They are detected by comparing the genomes of two related organisms that share a recent common ancestor, and determining if their have different:
- AT/GC genomic composition
- High rate of synonymous mutations for syntenic gene pairs
- Amino acid usage frequencies
- Codon usage frequencies
Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces fungi japonicus strain yFS275 and pombe 972h-
- Schizosaccharomyces pombe: model laboratory organism. Originally isolated from east African millet beer in 1893.
- Schizosaccharomyces japonicus: originally islated from strawberries near Kyusyu University, Japan in 1928.
| japonicus | pombe | |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 11,300,431 | 10,082,004 |
| GC% | 42.6 | 36 |
| AT% | 54.9 | 64 |
| CDS GC% | 45.5 | 39.5 |
| CDS AT% | 54.5 | 60.5 |
| Wobble GC% | 44.1 | 32.8 |
| Wobble AT% | 55.9 | 67.2 |
| Codon Usage Table | 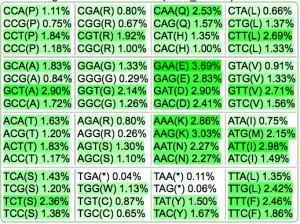 |
 |
| Codon Usage Table |  |
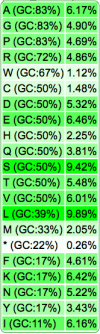 |
| Histogram of CDS GC content | 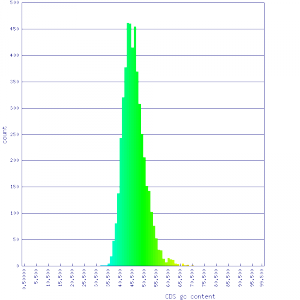 |
 |
| Histogram of CDS wobble position GC content | 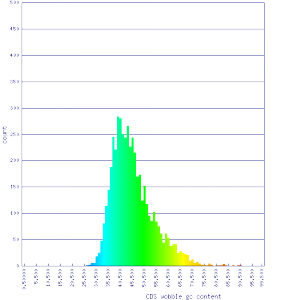 |
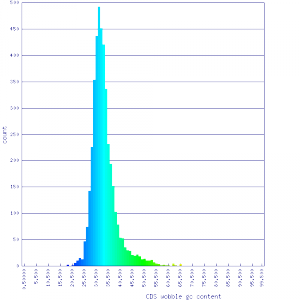 |
| Histogram of CDS GC content - wobble position GC content |  |
 |