SynMap2: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Background== | ==Background== | ||
SynMap2 is a major reworking of the original SynMap pairwise whole-genome synteny viewer. While the underlying computational framework remains the same, SynMap2 rethinks the visualizations by replacing static images with a high performance and interactive web-based dot-plot viewer. SynMap2’s interactive features allow researchers to explore the dataset from multiple angles in a significantly more intuitive way such as would be expected from the modern web. For example, subsets of syntenic matches can be selected by chromosomal regions or by subset ranges of mutation values (Kn, Ks, or Kn/Ks), and as subsets are selected, the visualization is automatically updated. The subset selection algorithms are designed to work efficiently even when faced with comparisons with many points (such as found in many polyploid species. Another improved feature is auto-persistance based coloring, where an algorithm can determine the most significant peaks at different sensitivity levels and apply unique colors to each, thus allowing researchers to visually distinguish between major duplication events. | SynMap2 is a major reworking of the original SynMap pairwise whole-genome synteny viewer. While the underlying computational framework remains the same, SynMap2 rethinks the visualizations by replacing static images with a high performance and interactive web-based dot-plot viewer. SynMap2’s interactive features allow researchers to explore the dataset from multiple angles in a significantly more intuitive way such as would be expected from the modern web. For example, subsets of syntenic matches can be selected by chromosomal regions or by subset ranges of mutation values (Kn, Ks, or Kn/Ks), and as subsets are selected, the visualization is automatically updated. The subset selection algorithms are designed to work efficiently even when faced with comparisons with many points (such as found in many polyploid species. Another improved feature is auto-persistance based coloring, where an algorithm can determine the most significant peaks at different sensitivity levels and apply unique colors to each, thus allowing researchers to visually distinguish between major duplication events. | ||
==Navigating the SynMap2 Viewer== | ==Navigating the SynMap2 Viewer== | ||
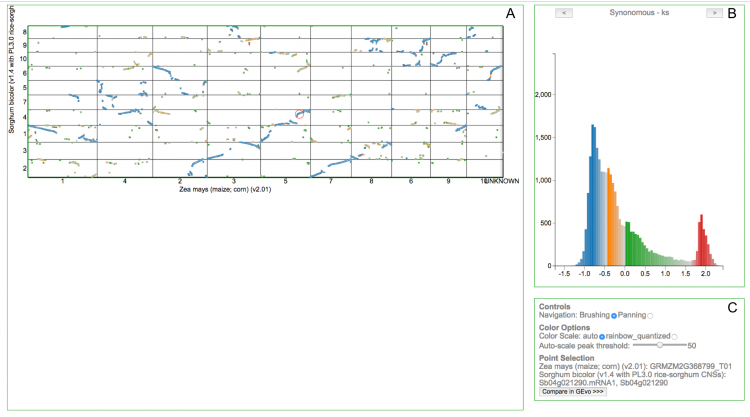
[[File: | [[File:synmap2_fig1.png|right|thumb|750px|'''Figure 1.''' SynMap2 interface.]] | ||
===Navigating the Dotplot=== | ===Navigating the Dotplot (Figure 1A)=== | ||
;Zoom | |||
===Navigating the Histogram=== | : Scroll (wheel or touch pad). | ||
;Pan | |||
: In 'Controls' (Fig. 1C), select 'Panning' then click & drag. | |||
;Select Subset of Points | |||
: In 'Controls' (Fig. 1C), select 'Brushing' then click & drag. Histogram will live update to represent values for only that subset. | |||
;Select Point | |||
: Click on point, selected point will be circled in red. Point information & a link to GEvo will become available under 'Point Selection' (Fig. 1C). | |||
;Change Coloring Between Ks, Kn, or Kn/Ks | |||
: Use arrows in histogram title (Fig. 1B). Histogram will also update. | |||
===Navigating the Histogram (Figure 1B)=== | |||
;Alternate Between Ks, Kn, or Kn/Ks Distributions. | |||
: Use arrows in histogram title. Point colors will also update to represent new histogram. | |||
;Focus on Subset Range of Values | |||
: Use mouse to 'brush' across histogram (click & drag). Dots with values outside this range will be dimmed to grey in the dotplot. | |||
;Move Subset Selector | |||
: Click & drag grey selector area. | |||
;Reset Subset Selector | |||
: Click outside grey selected area. | |||
;Adjust Color Scheme to Separate More/Less Peaks | |||
: Adjust 'Auto-scale peak threshold' under 'Color Options' (Fig. 1C). Lower numbers will differentiate more peaks. | |||
;Switch to Quantized Color View | |||
: Select 'rainbow-quantized' from 'Color Scale' (Fig. 1C). | |||
===Other Options=== | ===Other Options=== | ||
;Revert to The Old SynMap Viewer | |||
: Select "Legacy Version" tab at top of page | |||
==Example Analyses== | ==Example Analyses== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 70: | ||
==FAQ== | ==FAQ== | ||
;I was already used to the old version and want it back! | |||
: No worries. You can always switch back to the old version using the "Legacy Version" tab at the top of the page! | |||
;Who developed SynMap2? | |||
: The SynMap2 visualizer was written by Sean Stephens (https://github.com/seanastephens) of the University of Arizona Humans Data & Computers Lab (https://hdc-arizona.github.io/). Integration into CoGe was performed by Sean Davey & Asher Baltzell of the CoGe group. | |||
;Is SynMap2 visualizer open-source? | |||
: Absolutely! You can find the code [https://github.com/hdc-arizona/synteny-vis/ here] and [https://github.com/LyonsLab/coge here] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:46, 21 September 2016
Background
SynMap2 is a major reworking of the original SynMap pairwise whole-genome synteny viewer. While the underlying computational framework remains the same, SynMap2 rethinks the visualizations by replacing static images with a high performance and interactive web-based dot-plot viewer. SynMap2’s interactive features allow researchers to explore the dataset from multiple angles in a significantly more intuitive way such as would be expected from the modern web. For example, subsets of syntenic matches can be selected by chromosomal regions or by subset ranges of mutation values (Kn, Ks, or Kn/Ks), and as subsets are selected, the visualization is automatically updated. The subset selection algorithms are designed to work efficiently even when faced with comparisons with many points (such as found in many polyploid species. Another improved feature is auto-persistance based coloring, where an algorithm can determine the most significant peaks at different sensitivity levels and apply unique colors to each, thus allowing researchers to visually distinguish between major duplication events.
- Zoom
- Scroll (wheel or touch pad).
- Pan
- In 'Controls' (Fig. 1C), select 'Panning' then click & drag.
- Select Subset of Points
- In 'Controls' (Fig. 1C), select 'Brushing' then click & drag. Histogram will live update to represent values for only that subset.
- Select Point
- Click on point, selected point will be circled in red. Point information & a link to GEvo will become available under 'Point Selection' (Fig. 1C).
- Change Coloring Between Ks, Kn, or Kn/Ks
- Use arrows in histogram title (Fig. 1B). Histogram will also update.
- Alternate Between Ks, Kn, or Kn/Ks Distributions.
- Use arrows in histogram title. Point colors will also update to represent new histogram.
- Focus on Subset Range of Values
- Use mouse to 'brush' across histogram (click & drag). Dots with values outside this range will be dimmed to grey in the dotplot.
- Move Subset Selector
- Click & drag grey selector area.
- Reset Subset Selector
- Click outside grey selected area.
- Adjust Color Scheme to Separate More/Less Peaks
- Adjust 'Auto-scale peak threshold' under 'Color Options' (Fig. 1C). Lower numbers will differentiate more peaks.
- Switch to Quantized Color View
- Select 'rainbow-quantized' from 'Color Scale' (Fig. 1C).
Other Options
- Revert to The Old SynMap Viewer
- Select "Legacy Version" tab at top of page
Example Analyses
| Species 1 | Species 2 | Link |
|---|---|---|
| H. sapiens (human) | P. troglodytes (chimpanzee) | https://genomevolution.org/r/lg3o |
| H. sapiens (human) | C. familiaris (dog) | https://genomevolution.org/r/lknl |
| H. sapiens (human) | M. musculus (mouse) | https://genomevolution.org/r/lknm |
| A. thaliana | B. rapa | https://genomevolution.org/r/lknt |
| Z. mays (maize;corn) | S. bicolor (sorghum) | https://genomevolution.org/r/lknv |
| O. niloticus (Nile tilapia) | S. salar (Atlantic salmon) | https://genomevolution.org/r/lkoj |
| E. coli (MG1655) | E. coli (DH10B) | https://genomevolution.org/r/lkng |
FAQ
- I was already used to the old version and want it back!
- No worries. You can always switch back to the old version using the "Legacy Version" tab at the top of the page!
- Who developed SynMap2?
- The SynMap2 visualizer was written by Sean Stephens (https://github.com/seanastephens) of the University of Arizona Humans Data & Computers Lab (https://hdc-arizona.github.io/). Integration into CoGe was performed by Sean Davey & Asher Baltzell of the CoGe group.
- Is SynMap2 visualizer open-source?
- Absolutely! You can find the code here and here