Pan-grass synteny: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Pan-grass-species-tree.png|thumb|right|500px|Phylogeny of evolutionary relationships of sequenced grass genomes. Radiation of grass family, poaceae is dated to have occurred 70 | [[Image:Pan-grass-species-tree.png|thumb|right|500px|Phylogeny of evolutionary relationships of sequenced grass genomes. Radiation of grass family, poaceae is dated to have occurred 50-70 million years before present, in line with the date for the pan-grass’ shared ancient whole genome duplication. Soon after the Panicoideae (Zm-Sb) and Ehrhartoideae (Os-Bd) clades diverged, Os and Bd diverged (~49MYA). Zm and Sb diverged ~11MYA, followed immediately by a specific whole genome duplication event in Zm’s lineage. Red stars indicate [[whole genome duplication events]]. ]] | ||
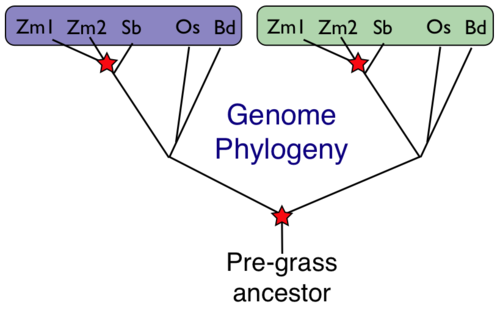
[[Image:Pan-grass-genome-tree.png|thumb|right|500px|Expanded genome phylogeny of sequenced grass genomes. Given the pre-grass whole genome duplication event and the Zm specific whole genome duplication event, there are 10 effective genomes for the 4 sequenced grass genomes: 2xBd, 2xOs, 2xSb, 4xZm. Each of these whole genome duplication events contemporaneously creates a duplicate copy of every chromosome and all the underlying genomic features and genes. However, over evolutionary time, many duplicated genes are lost from one [[homeologous]] region or its partner through a process known as [[fractionation]]. Red stars indicate [[whole genome duplication events]]. ]] | [[Image:Pan-grass-genome-tree.png|thumb|right|500px|Expanded genome phylogeny of sequenced grass genomes. Given the pre-grass whole genome duplication event and the Zm specific whole genome duplication event, there are 10 effective genomes for the 4 sequenced grass genomes: 2xBd, 2xOs, 2xSb, 4xZm. Each of these whole genome duplication events contemporaneously creates a duplicate copy of every chromosome and all the underlying genomic features and genes. However, over evolutionary time, many duplicated genes are lost from one [[homeologous]] region or its partner through a process known as [[fractionation]]. Red stars indicate [[whole genome duplication events]]. ]] | ||
The grass family of plants, [http://www.mobot.org/MOBOT/research/APweb/orders/poalesweb.htm#Poaceae poaceae], radiated 50-70 million years, around the time that dinosaurs were going extinct and mammals were one the rise. Today, they are one of the largest families of plants with worldwide distribution. Several members of poaceae are agronomically important, being major sources of food for the majority of human populations. As such, they are the center of much applied and basic scientific research. | |||
Revision as of 23:47, 11 March 2010

The grass family of plants, poaceae, radiated 50-70 million years, around the time that dinosaurs were going extinct and mammals were one the rise. Today, they are one of the largest families of plants with worldwide distribution. Several members of poaceae are agronomically important, being major sources of food for the majority of human populations. As such, they are the center of much applied and basic scientific research.