Intercalated synteny: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Created page with '[[Image:Fractionation-cartoon.png|thumb|center|600px|Cartoon of fractionation following a genome duplication event. Colored circle represent genes along a genomic region. Followi...' |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
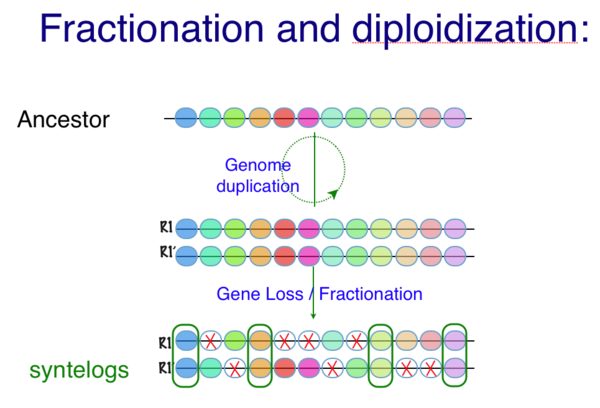
[[Image:Fractionation-cartoon.png|thumb|center|600px|Cartoon of fractionation following a genome duplication event. Colored circle represent genes along a genomic region. Following a genome duplication, all genomic content including chromosomes and their underlying gene content is contemporaneously copied. Over evolutionary time, many duplicate genes (but not all) are lost from one homeologous region or its partner region. This returns the overall gene content of a genome to one that is more similar to the pre-duplicated ancestor, but the overall genomic structure has changed drastically. Genes that are retained in duplicate can be used to detect synteny by their collinear arrangement in two or more genomic regions. ]] | |||
Intercalated Synteny is observed by comparing a genome that has undergone a [[whole genome duplication]] followed by [[fractionation]] to an outgroup syntenic region that has not undergone fractionation. Members of syntenic gene pairs in the outgroup region are intercalated with regards to the fractionated genomic regions. | |||
[[Image:Fractionation-cartoon.png|thumb|center|600px|Cartoon of fractionation following a genome duplication event showing intercalated synteny. Colored circle represent genes along a genomic region. Following a genome duplication, all genomic content including chromosomes and their underlying gene content is contemporaneously copied. Over evolutionary time, many duplicate genes (but not all) are lost from one homeologous region or its partner region. This returns the overall gene content of a genome to one that is more similar to the pre-duplicated ancestor, but the overall genomic structure has changed drastically. Genes that are retained in duplicate can be used to detect synteny by their collinear arrangement in two or more genomic regions. ]] | |||
[[Image:At-Cp-Fractionation.png|thumb|center|600px|Example GEvo analysis of fraction of gene content between 4 syntenic regions of Arabidopsis thaliana and one syntenic region of Carica papaya. Papaya is in the middle with 2 Arabidopsis regions above and below. Since their divergence, Arabidopsis thaliana has had two whole genome duplication events while papaya has had none. After each whole genome duplication event in Arabidopsis, duplicated genes are lost from one homeologous region or the other. Thus, this single region of papaya contains nearly the entire gene content of the four syntenic Arabidopsis regions. Note that some families of genes are retained preferentially following a whole genome duplication event, and that some genes transpose. This analysis can be regenerated at: http://tinyurl.com/o6xnea .]] | [[Image:At-Cp-Fractionation.png|thumb|center|600px|Example GEvo analysis of fraction of gene content between 4 syntenic regions of Arabidopsis thaliana and one syntenic region of Carica papaya. Papaya is in the middle with 2 Arabidopsis regions above and below. Since their divergence, Arabidopsis thaliana has had two whole genome duplication events while papaya has had none. After each whole genome duplication event in Arabidopsis, duplicated genes are lost from one homeologous region or the other. Thus, this single region of papaya contains nearly the entire gene content of the four syntenic Arabidopsis regions. Note that some families of genes are retained preferentially following a whole genome duplication event, and that some genes transpose. This analysis can be regenerated at: http://tinyurl.com/o6xnea .]] | ||
Revision as of 13:40, 6 February 2012
Intercalated Synteny is observed by comparing a genome that has undergone a whole genome duplication followed by fractionation to an outgroup syntenic region that has not undergone fractionation. Members of syntenic gene pairs in the outgroup region are intercalated with regards to the fractionated genomic regions.