GEvo: Difference between revisions
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
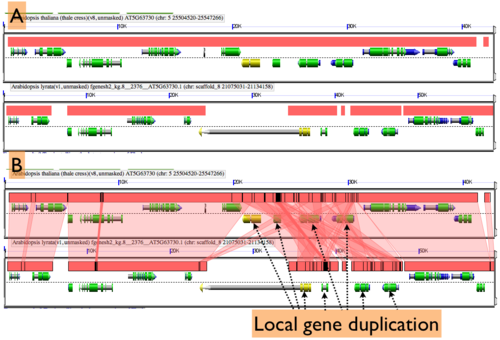
[[Image:GEvo-local-dup-no-show-overlap.png|thumb|500px|right|Example of GEvo result with local duplications that are obfuscated by not showing separating overlapping HSPs. Comparison is between orthologous regions of Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. (A) No wedges drawn connecting regions of sequence similarity. (B) Wedges drawn connecting regions of sequence similarity. Note the "messy" regions where the local duplication is. Results can be regenerated at http://tinyurl.com/mokdnn .]] | [[Image:GEvo-local-dup-no-show-overlap.png|thumb|500px|right|Example of GEvo result with local duplications that are obfuscated by not showing separating overlapping HSPs. Comparison is between orthologous regions of Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata. (A) No wedges drawn connecting regions of sequence similarity. (B) Wedges drawn connecting regions of sequence similarity. Note the "messy" regions where the local duplication is. Results can be regenerated at http://tinyurl.com/mokdnn .]] | ||
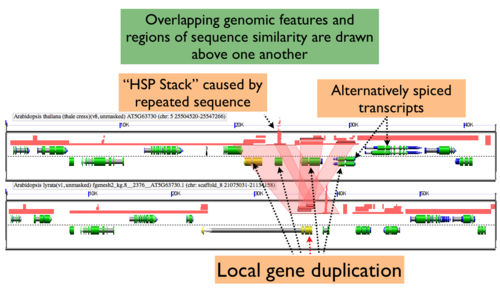
[[Image:GEvo-local-dup-show-overlap.png|thumb|500px|right|]] | [[Image:GEvo-local-dup-show-overlap.png|thumb|500px|right|vo results with "auto adjust" HSP and Genomic Features turned on. This causes GEvo to find genomic features and blast-hits that overlap at the same position, and drawn them such that they are separated in order to identify local duplications in a genomic region, repeat sequences, and alternatively spliced transcripts. This is a comparison between orthologous regions of Arabidopsis thaliana and Arabidopsis lyrata, and can be regenerated at http://tinyurl.com/mokdnn. Wedges have been drawn connection regions of sequence similarity between one gene in the bottom panel. This shows that this one gene has sequence similar to four regions in the orthologous genomic region, which is indicative of a local gene duplication. Also, there is a "stack" of HSPs which is caused by repeated sequences. Note that two genes have annotations for being alternatively spliced, which is visualized by separating the drawing of overlapping genomic features. ]] | ||
By default GEvo will drawn overlapping genomic features and regions of sequence similarity on top of one another. However, this sometimes hides some of the interesting complexities in a genomic region such as local duplications or regions containing repeated sequences. To view these, select the "Results Parameters" tab and select "Yes" for "Auto adjust overlapping features" and/or "Auto adjust overlapping HSPs". These options are set to "No" by default because finding and drawing overlapping features can take a long time to process, and are not always useful. | By default GEvo will drawn overlapping genomic features and regions of sequence similarity on top of one another. However, this sometimes hides some of the interesting complexities in a genomic region such as local duplications or regions containing repeated sequences. To view these, select the "Results Parameters" tab and select "Yes" for "Auto adjust overlapping features" and/or "Auto adjust overlapping HSPs". These options are set to "No" by default because finding and drawing overlapping features can take a long time to process, and are not always useful. | ||
Revision as of 19:03, 10 August 2009
 | |
 Typical GEvo Analysis | |
| Software company | CoGe Team |
|---|---|
| Analysis Type | Compare multiple genomic regions for synteny and other forms of genome evolution |
| Working state | Released |
| Tools Utilized | blastn, tblastx, blastz, CHAOS, LAGAN, DiAlign 2 |
| Website | http://synteny.cnr.berkeley.edu/CoGe/GEvo.pl |
GEvo is CoGe's Genome Evolution Analysis tool, designed to visually compare genomic regions using both local and global alignment algorithms.
Introduction
The purpose of GEvo is to compare multiple genomic regions from any number of organisms using a variety of different sequence comparison algorithms in order to quickly identify patterns of genome evolution
Alignment Algorithms
Current GEvo can use:
- BlastZ: DNA-DNA Local Alignment Algorithm. Good for finding large regions of conserved sequence.
- BlastN: DNA-DNA Local Alignment Algorithm. Good for finding small regions of conserved sequence.
- TBlastX: Translated DNA-Translated DNA Local Alignment Algorithm. Good for finding small regions of divergent, but evolutionarily conserved, genomic sequence where protein translated sequence is more conserved than DNA sequence.
- Chaos: DNA-DNA Local Alignment Algorithm. Good for finding small regions of conserved sequence. Uses fuzzy matches so it can seed its alignment on small sequences than BlastN. However, it is slower than BlastN.
- DiAlign: DNA-DNA Global Alignment Algorithm. Global alignment can be seeded using local alignment algorithm. Good for alignment the entire sequence.
GEvo supports using Chaos, BlastN, and BlastZ for seeding DiAlign.
- Lagan: DNA-DNA Glocal Alignment. Using a hybrid alignment approach.
Regenerating/Saving a GEvo Analysis
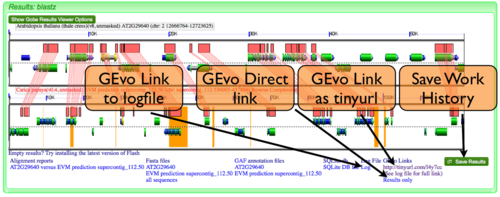
GEvo Links
After results are generated by GEvo, a URL will be created that will be a hyperlink to GEvo with your analysis pre-configured. To regenerated the results, all you need to do is press the "Run GEvo Analysis!" button and wait for the analysis to run. This link is stored in two places:
- At the bottom of the results under "GEvo Links" (see example image.) This link has been condensed using the tinyurl redirecting service.
- At the bottom of the log file. The link to the log file can also be found at the bottom of the results (see example image.)
GEvo Direct
GEvo Direct is a tool for quickly viewing the results of a previously run analysis without having to re-run the analysis. Please Note: CoGe saves all the files from a GEvo analysis for ~24 hours. After that time, the data-files are deleted and the GEvo Direct link will no longer work.
Save Work History
Registered CoGe users can save a link to a GEvo analysis for later retrieval from their work history. This permits a GEvo analysis to also be names and annotated for future reference.
Modifying result graphics
Showing Contigs

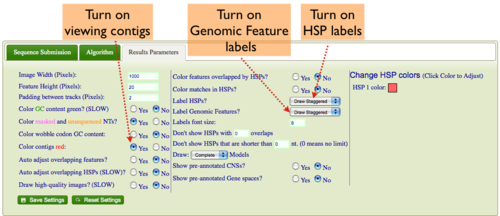
Some genomes have contig assembly information. To view this in GEvo's results:
- Select the "Results Parameters" tab from GEvo's configuration box
- Select "yes" for the option "Color contigs red".
Turning on labels for HSPs (blast hits) in GEvo's results
If you want to have the HSP number drawn on the HSP:
- Select the "Results Parameters" tab from GEvo's configuration box
- Select "yes" for the option "Label HSPs".
- You can have the labels drawn linearly, so each label is at the same vertical position for a track, or staggered, where they are drawn top, middle, bottom alternating.
Turning on labels for Genomic Features (e.g. genes) in GEvo's results
If you want to have the feature names drawn on the feature:
- Select the "Results Parameters" tab from GEvo's configuration box
- Select "yes" for the option "Label Genomic Features".
- You can have the labels drawn linearly, so each label is at the same vertical position for a track, or staggered, where they are drawn top, middle, bottom alternating.
Expanding Overlapping Features and Regions of Sequence Similarity
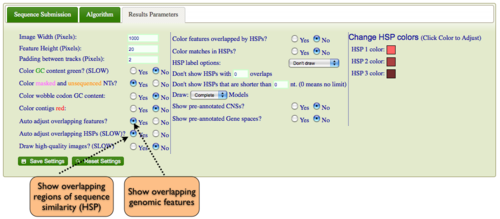
By default GEvo will drawn overlapping genomic features and regions of sequence similarity on top of one another. However, this sometimes hides some of the interesting complexities in a genomic region such as local duplications or regions containing repeated sequences. To view these, select the "Results Parameters" tab and select "Yes" for "Auto adjust overlapping features" and/or "Auto adjust overlapping HSPs". These options are set to "No" by default because finding and drawing overlapping features can take a long time to process, and are not always useful.