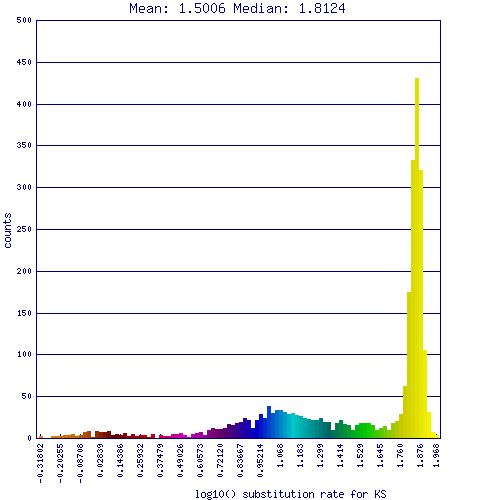
GC content shift
GC content shift is an evolutionary genome-wide change in the GC content of an organism. The evolutionary consequences of such a change is unknown. They are detected by comparing the genomes of two related organisms that share a recent common ancestor, and determining if their have different:
- AT/GC genomic composition
- High rate of synonymous mutations for syntenic gene pairs
- Amino acid usage frequencies
- Codon usage frequencies
Comparison of Schizosaccharomyces fungi japonicus strain yFS275 and pombe 972h-
| japonicus | pombe | |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 11,300,431 | 10,082,004 |
| GC% | 42.6 | 36 |
| AT% | 54.9 | 64 |
| CDS GC% | 45.5 | 39.5 |
| CDS AT% | 54.5 | 60.5 |
| Wobble GC% | 44.1 | 32.8 |
| Wobble AT% | 55.9 | 67.2 |
| Codon Usage Table | 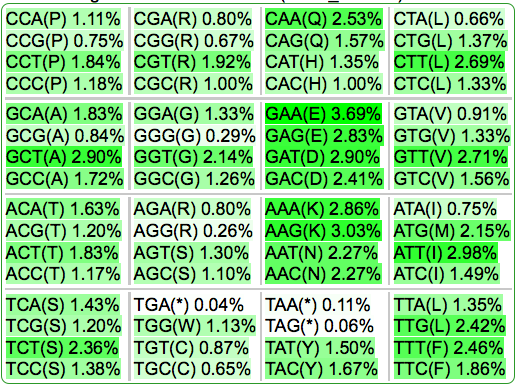 |
67.2 |