Jcvi code
Background
Rumor has it that there is a code in one of the synthetic genomes by JCVI. Supposedly, this code contains an email address.
Synthetic JCVI genomes in CoGe
- synthetic Mycoplasma genitalium strain JCVI-1.0: http://genomevolution.org/CoGe/OrganismView.pl?oid=35986
- synthetic Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn1.0: http://genomevolution.org/CoGe/OrganismView.pl?oid=35385
Closest natural relatives
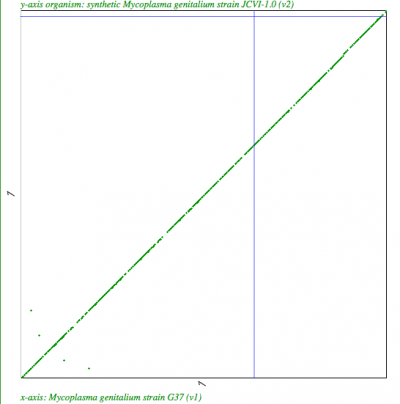
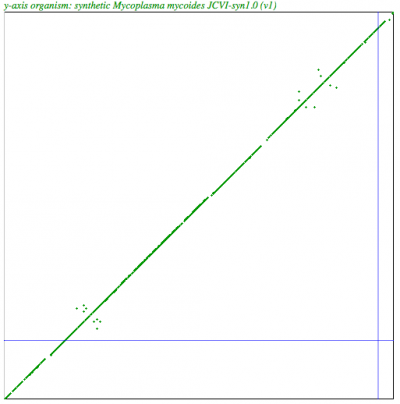
| Syntenic dotplot of synthetic Mycoplasma genitalium strain JCVI-1.0 (y-axis) v. Mycoplasma genitalium strain G37 (x-axis) http://genomevolution.org/r/4mx1 | Syntenic dotplot of synthetic Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn1.0 (y-axis) v. Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. capri strain GM12 (x-axis) http://genomevolution.org/r/4mx2 |
|
|
GEvo Analyses: high-resolution detection of syntenic discontinuities
Genitalium


- Disrupted WT gene: MG_408 , NP_073081.1 , pmsR
- methionine sulfoxide reductase A
- this stereospecific enzymes reduces the S isomer of methionine sulfoxide while MsrB reduces the R form a fusion protein of this enzyme with MsrB provides protection against oxidative stress in Neisseria gonorrhoeae this stereospecific enzymes reduces the S isomer of methionine sulfoxide while MsrB reduces the R form
- Inserted gene: ABY79711.1 , MGATCC33530_0530
- bifunctional AAC/APH (AAC(6'): 6'-aminoglycoside N-acetyltransferase and APH(2'): 2-aminoglycoside phosphotransferase
- Aminoglycoside antibiotic resistance is largely the result of the production of enzymes that covalently modify the drugs including kinases (Aph) with structural and functional similarity to protein and lipid kinases. One of the most important aminoglycoside resistance enzymes is Aac(6')-Aph(2), a bifunctional enzyme with both aminoglycoside acetyltransferase and kinase activities.
Mycoides
Whole genome GEvo analysis: http://genomevolution.org/r/4mx4 (need higher res monitor to take a screen shot that show discontinuities.)