FractBias
Background
Whole genome duplications (WGDs) and genome fractionation are covered more thoroughly in other CoGepedia entries. In short, WGDs create two or more copies of a genome: which are referred to as subgenomes. The duplicate subgenomes then undergo gene loss in a process called fractionation which is part of returning to a diploid state, diploidization. All things being equal, one may assume that fractionation would occur randomly across the redundant genes created after a WGD, however bias towards gene loss on one genome, called fractionation bias, has been observed in several species including: maize [1], Brassica rapa [2], and rainbow trout [3].
The FractBias code and an example data set can be found on GitHub
Overview
[[File:|right|thumb|900px|Figure 1. A demonstration of which genes are included in the FractBias analysis of retained genes when the include "All genes" setting is selected. All genes that exist on target genome chromosomes will be used to determine the sliding window size and calculate the number of retained genes on query chromosomes.]] [[File:|right|thumb|900px|Figure 2. A demonstration of which genes are included in the FractBias analysis of retained genes when the include "Only retained genes" is selected. Genes unique to either the target or to the query genome will not be considered in either the window size or in calculating the number of retained genes within in the window.]]
What goes in
- Two assembled genomes that have annotated coding sequences (CDS)
- A syntenic ratio set by the user (identified by empiric tests outside of the FractBias tool)
- The genome with a lower ratio will be the target genome
- The genome with a higher ratio will be the query genome
- The full GFF of the target genome
- The syntenic blocks identified by SynMap
- Setting defined by the user
- What genes should be counted
- Count all genes present on the target genome (refer to Figure 1)
- Only count genes that are retained in both genomes (refer to Figure 2)
- Target chromosome number
- Query chromosome number
- Window size
- What genes should be counted
Data files passed in
- SynMap DAGChainer output: comparison_name.aligncoords.gcoords
- GFF file for target genome
What comes out
- A figure containing a subplot for every target genome chromosome
- Links to the raw data used to create the subplots
Biological Examples
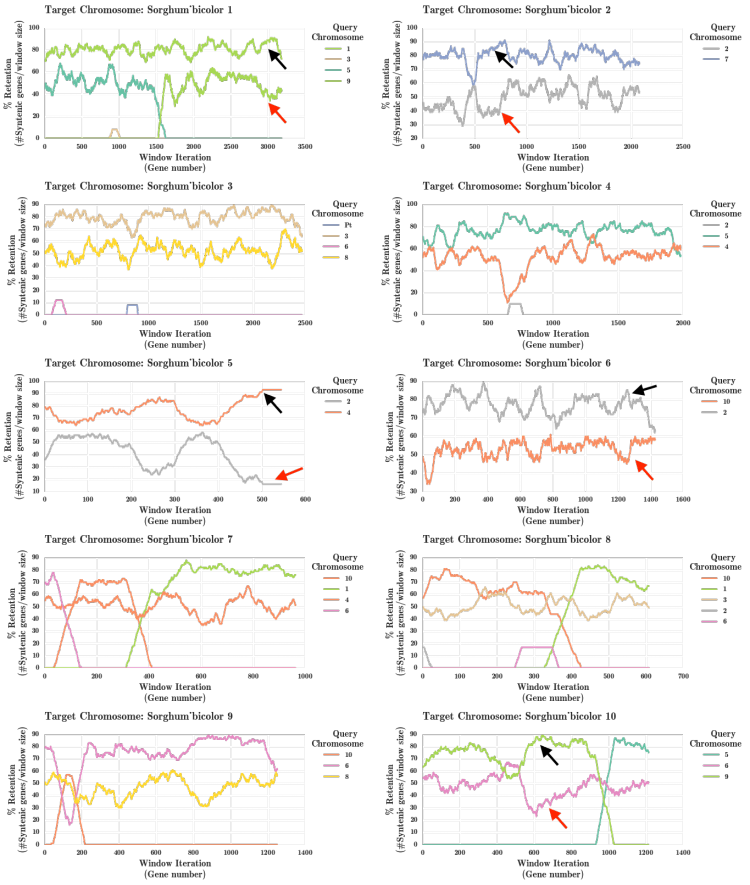
Sorghum and Maize Fractionation Bias
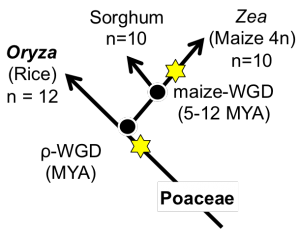
The fractionation bias in the maize genome has been previously studied[4] independently. This analysis was rerun using the FractBias tool.
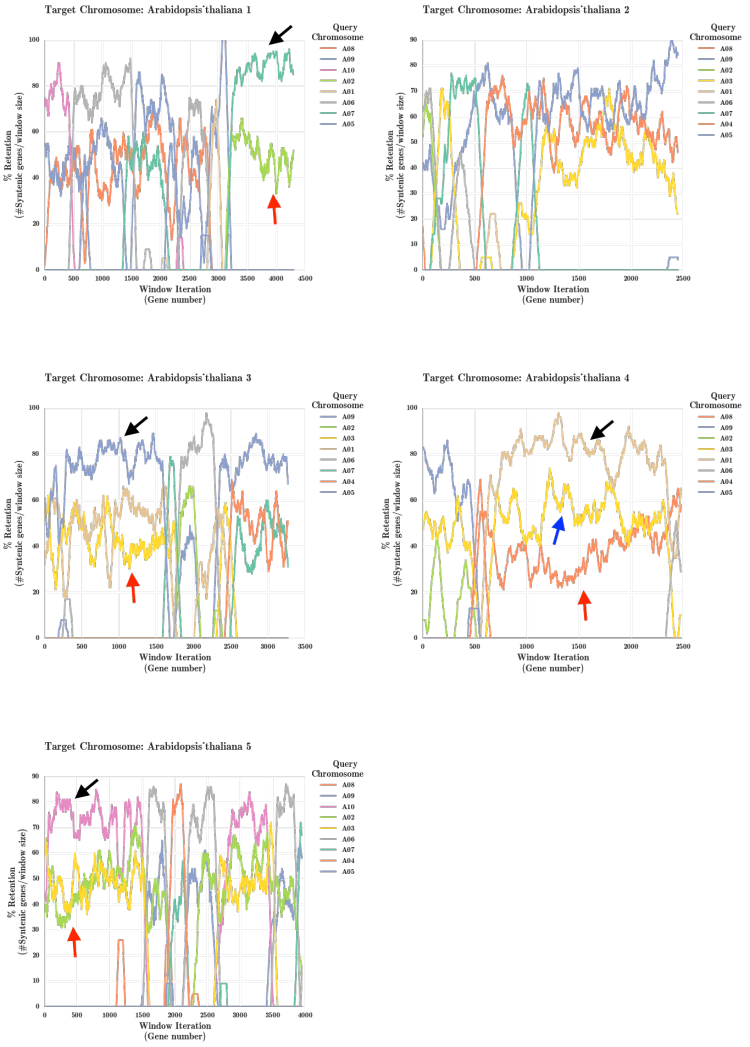
Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica rapa Fractionation Bias
| Table 1. FractBias examples available through CoGe’s SynMap. Syntenic depth ratios range from 1:1 to 1:6 using two species of plasmodia, two mammals, and six species of plants to highlight the flexibility and ease of use of FractBias. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Species | Query Species | Syntenic Depth Ratio | Link to 'All Genes' Analysis | Link to 'Only Syntenic Genes' Analysis | |
| Plasmodium falciparum | Plasmodium knowlesi | 1:1 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7j6 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7km | |
| Homo sapiens | Pan troglodytes | 1:1 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k813 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k811 | |
| Sorghum bicolor | Zea mays | 1:2 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7jx | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7j3 | |
| Brassica rapa | Brassica napus | 1:2 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7mw | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7k3 | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Brassica rapa | 1:3 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7jq | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7jg | |
| Vitis vinifera | Arabidopsis thaliana | 1:4 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7p1 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7ov | |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | Brassica napus | 1:6 | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7qz | https://genomevolution.org/r/k7r6 | |
References
- ↑ Schnable, J.C. et al. Dose–sensitivity, conserved non-coding sequences, and duplicate gene retention through multiple tetraploidies in the grasses. Front. Plant Sci. http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2011.00002 (2011)
- ↑ Cheng, F. et al. Biased gene fractionation and dominant gene expression among the subgenomes of Brassica rapa. PLOS ONE DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036442 (2012)
- ↑ Berthelot, C. et al. The rainbow trout genome provides novel insights into evolution after whole-genome duplication in vertebrates. Nature Communications 5: DOI:10.1038/ncomms4657 (2014)
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Schnable, J. C. et al. Differentiation of the maize subgenomes by genome dominance and both ancient and ongoing gene loss. PNAS 108:4069-4074