UGTs through the genus Brassica
Introduction
The genus Brassica
The genus Brassica consists of over thirty wild species and hybrids or morphotypes. Generally, species from the genus Brassica are used in food like broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage and more.
The Brassica genome has undergone more polyploidy than Arabidopsis thaliana. Arabidopsis thaliana is notable for being a model organism because of its complexity paired with a relatively small genome.
Duplication Events
The Brassica genome has undergone two tetraploidy and two hexaploidy events, one more than Arabidopsis, since the eudicot paleohexaploidy event which gave rise to Vitis, Prunus, Arabidopsis, and Brassica.
Triangle of U
The "Triangle of U" theory describes the genetic relationship between six species of Brassica: Brassica rapa, Brassica nigra, Brassica oleracea, Brassica juncea, Brassica carinata, and Brassica napus. B. juncea, B. carinata and B. napus are allotetraploids, hybrids with four times the chromosome set of haploids. 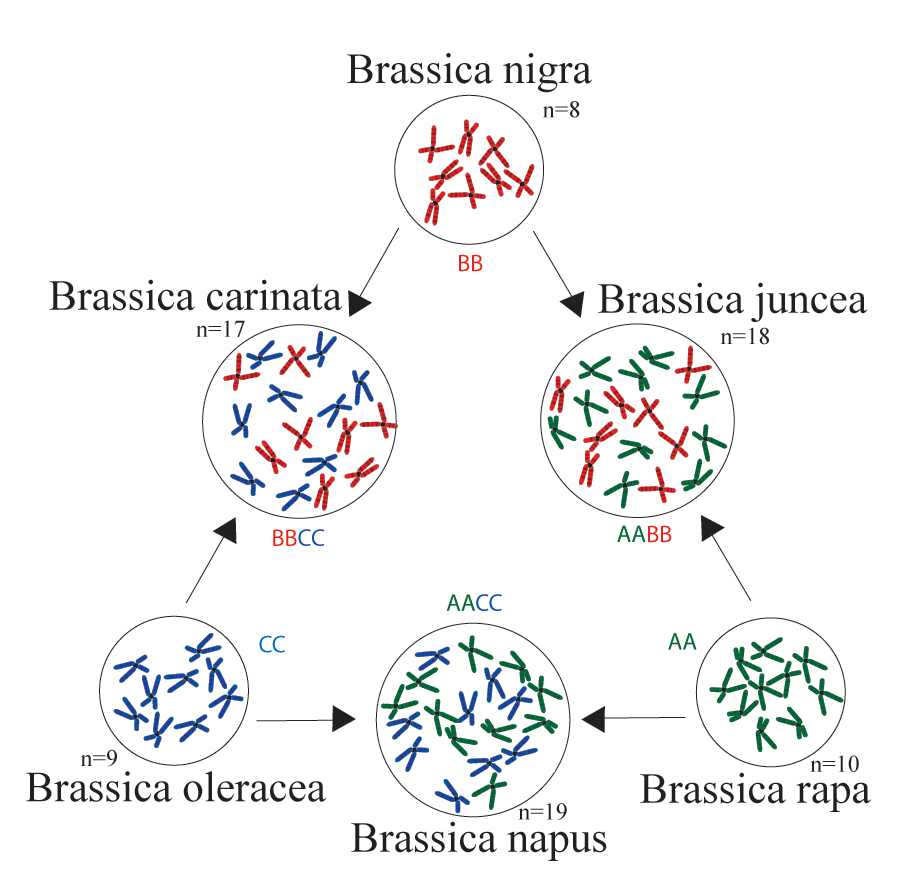
UGT Gene Family
UGT functions
Uridine diphosphate (UDP) glycosyltransferases (UGTs) mediate transfer of glycosyl residues from activated nucleotide sugars to acceptor molecules (Tang, Unleashing the Genome of the Brassica rapa). They provide instructions for making enzymes that perform the process of glucuronidation, the addition of glucuronic acid to a substrate (Genetics Home Reference, UGT gene family).
UGT chemistry
By mediating transfer of glycosyl residues from activated nucleotide sugars to acceptor molecules, UGTs regulate properties of those acceptors such as bioactivity, solubility and transport within cells and throughout organisms (Ross, Higher plant glycosyltransferases).
Methods
Building a Phylogeny of Genes in the UGTs in Arabidopsis thaliana
CoGe BLAST
TAIR
Glycosyltransferase Family 1 on The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) contained each annotation by the The Institute for Genomic Research (TIGR) for flavonols and anthocyanidins which contribute to plant pigmentation. CoGe BLAST was used to find sequences corresponding to those in TAIR. After a little coding, we were able to identify from a list of over a hundred which were from the TAIR database and which were from CoGe with ease. Information including genomic locus, TIGR Annotation and Accession are in appropriately named csv files.
The FASTA sequence for gene At5g65550 was used as a query sequence in the JGI Phytozome database to recover Arabidopsis lyrata genes.
The Brassica Database (BRAD) was used to recover orthologs for the identifies Arabidopsis thaliana genes.
Organizing the Data
A table was developed to organize the information collected from each database (CoGe, Phytozome, BRAD). 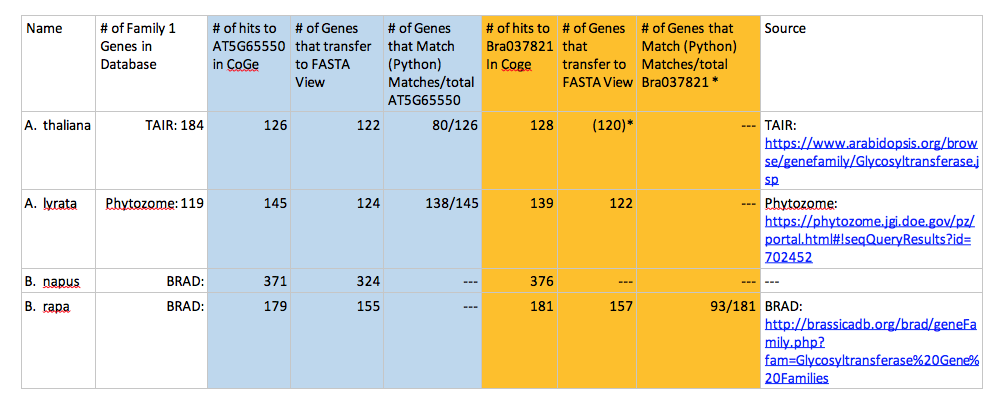
The table above tracks how the size of data changed along the process of collecting the FASTAs. The blue section of the table denotes information relative to the gene At5g65550 while the orange section of the table denotes information relative to the Brassica rapa ortholog to At5g65550, Bra037821.