Syntenic depth: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
These tables show the number of gene participating at a particular syntenic depth and are used to infer the number of polyploidy events between two genomes. | These tables show the number of gene participating at a particular syntenic depth and are used to infer the number of polyploidy events between two genomes. | ||
{| width="200" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1" border="1" | |||
|- | |||
| Syntenic Dopltot | |||
| Syntenic Depth Calculation | |||
| Known History | |||
|- | |||
| [[Image:Screen shot 2012-03-27 at 2.53.56 PM.png|400px]] | |||
| [[Image:Screen shot 2012-03-28 at 8.48.43 AM.png|300px]] | |||
| | |||
Obvious 2:2 depth. | |||
Share a recent whole genome duplication. Also share older whole genome duplictions (at least one) | |||
|} | |||
<br> | <br> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:08, 31 May 2012
Syntenic depth refers to the number of times a genomic region (or genome) is syntenic to regions in another genome.
Tools in CoGe for classifying and quantitating syntenic depth:
Examples:
| Organism | Syntenic Depth |
Dotpot |
| E. coli DH10B to MG1655 |
1:1 |
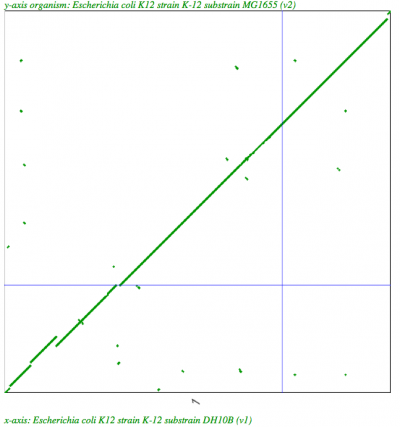 |
| Human-Chimp | 1:1 | 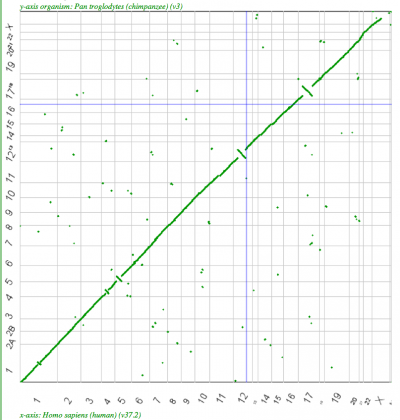
|
| Rice-Brachypodium |
2:2 |
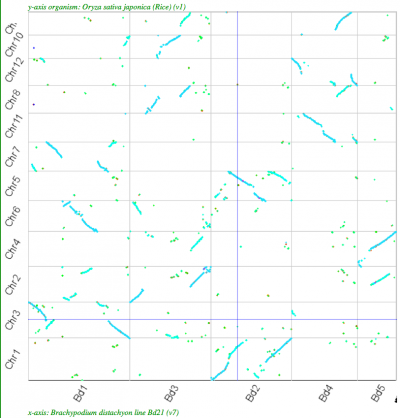 |
| Sorghum-Maize | 2:4 | 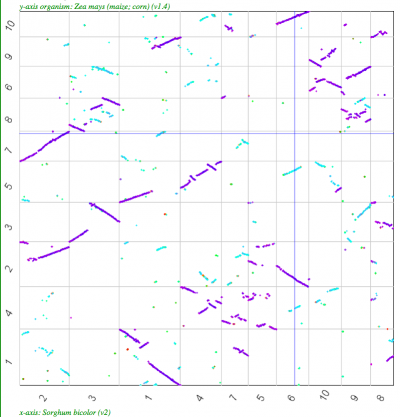
|
Syntenic Depth Tables
SynFind Syntenic Depth Examples
These tables show the number of gene participating at a particular syntenic depth and are used to infer the number of polyploidy events between two genomes.
| Syntenic Dopltot | Syntenic Depth Calculation | Known History |

|

|
Obvious 2:2 depth. Share a recent whole genome duplication. Also share older whole genome duplictions (at least one) |