Difference between revisions of "Ramosa2 orthologs and CNSs"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Image:NM_001138446.png|thumb|600px| | + | =A CoGe Walkthrough – ramosa2 ortholog identification and CNS analysis= |
| − | [[Image:Ra2-CoGeBlast.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
| − | [[Image:CoGeBlast-HSPTable.png|thumb|600px| | + | In this exercise you will use genomic synteny to identify putative ramosa2 orthologs across several cereal genomes. In addition you will identify Conserved Non-Coding Sequences (CNSs) in the ramosa2 promoter region. |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-manual-add-sequence.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
| − | [[Image:Ra2-GEvo-result.png|thumb|600px| | + | [[Image:NM_001138446.png|thumb|600px|center|GenBank Accession NM_001138446 from NCBI]] |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-direct-submission-check.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-reverse-complement-option.png|thumb|600px| | + | First we need to get some ra2 sequence to use in CoGe Blast. Search the NCBI nucleotide database for: NM_001138446. Copy the Fasta sequence of the mRNA. |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-sequence-needs-rc.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-add-to-all.png|thumb|600px| | + | Now go to the website for CoGe: http://synteny.cnr.berkeley.edu/CoGe/ (you can just google CoGe and you’ll see it a few pages down). Click on “CoGe Blast” and paste your sequence in the “Sequences field”. It is not necessary to have a Fasta header but it helps keep track of things. |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-change-region-extent.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
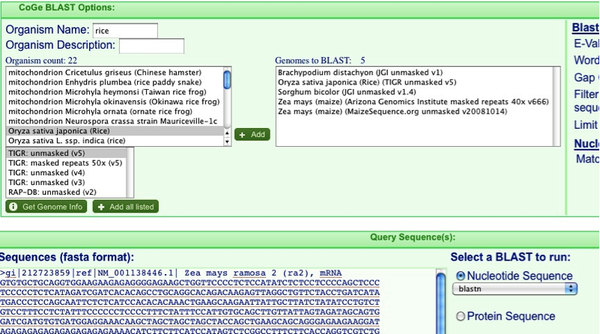
| − | [[Image:GEvo-identifying-conserved-sequence-ra2.png|thumb|600px| | + | Now we need to decide which organisms we will Blast. Only (mostly) completed genome sequences are available from this window (more on how to add other sequences later on). In the “Organism Name” field search for Sorghum, Rice, Zea mays, and Brachypodium and add them in turn by hitting the “+add” button. I find that it is best to add both the pseudomolecule maize sequence as well as the sequenced BACs as shown in the picture below. Make sure you don’t accidently add the chloroplast genomes instead of the nuclear! |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-blastn.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-ra2-cns-discovery.png|thumb|600px| | + | [[Image:Ra2-CoGeBlast.png|thumb|600px|center|Configuring CoGeBlast to search multiple grass genomes]] |
| − | [[Image:GEvo-image-parameters-hsp-limit.png|thumb|600px| | + | |
| + | When you’re ready, hit “Run CoGe Blast” to start your analysis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Note, this is just like Blast, only you are blasting several whole genome sequences at the same time. You can enter protein sequences, change the Blast algorithm and adjust parameters just as you would in any Blast analysis. | ||
| + | |||
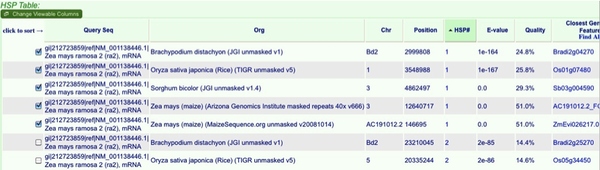
| + | Your results will show both the genomic locations and a table of the “blast hits” or high scoring pairs (HSPs). The HSPs are initially ordered by organism, but you can order them by any of the criteria at the top. To sort HSPs by multiple criteria simply hit one criteria then hold shift while selecting another. I often sort by HSP# then organism. This will give you the top hits in all blasted genomes. You can evaluate the results much like any blast analysis. At this point we will pick which genomic locations to examine for gene synteny. Select the top hit from each genome. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:CoGeBlast-HSPTable.png|thumb|600px|center|HSP Table from CoGeBlast. HSPs are commonly known as "Blast Hits"]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-manual-add-sequence.png|thumb|600px|center|Manually adding a sequence to a GEvo analysis by pasting in a sequence into the sequence submission box]] | ||
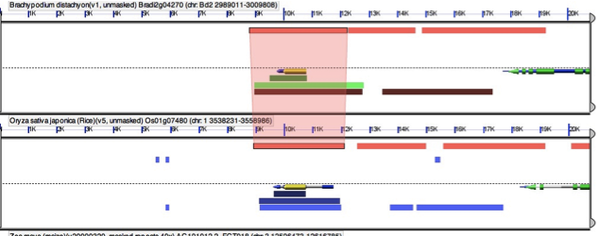
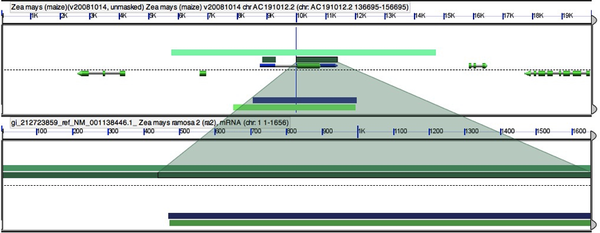
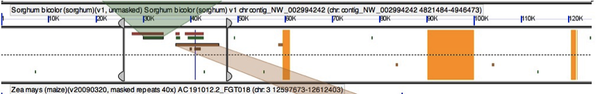
| + | [[Image:Ra2-GEvo-result.png|thumb|600px|center|GEvo result of ra2 in syntenic region between Brachypodium and Rice]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-direct-submission-check.png|thumb|600px|center|Checking a direct sequence submission in GEvo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-reverse-complement-option.png|thumb|600px|center|Selecting the reverse complement option for a sequence submission in GEvo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-sequence-needs-rc.png|thumb|600px|center|Identifying a sequence that needs to be reverse complemented in GEvo]] | ||
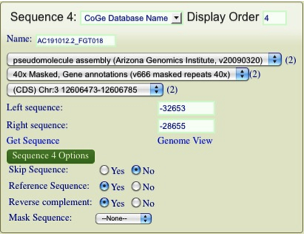
| + | [[Image:GEvo-add-to-all.png|thumb|600px|center|Option increase up and downstream sequence to all sequence submissions]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-change-region-extent.png|thumb|600px|center|Changing the amount of up and downstream sequence for a sequence submission in GEvo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-identifying-conserved-sequence-ra2.png|thumb|600px|center|Identifying conserved sequence around ramora2 in GEvo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-blastn.png|thumb|600px|center|Selecting blastn in GEvo]] | ||
| + | [[Image:GEvo-ra2-cns-discovery.png|thumb|600px|center|Using blastn in GEvo to identify conserved noncoding sequences for ramora2 in grasses]] | ||
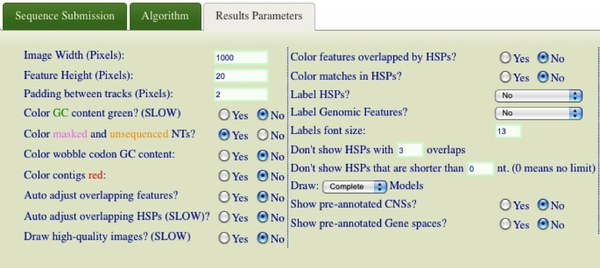
| + | [[Image:GEvo-image-parameters-hsp-limit.png|thumb|600px|center|Setting HSP limits in GEvo]] | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 15 October 2009
A CoGe Walkthrough – ramosa2 ortholog identification and CNS analysis
In this exercise you will use genomic synteny to identify putative ramosa2 orthologs across several cereal genomes. In addition you will identify Conserved Non-Coding Sequences (CNSs) in the ramosa2 promoter region.
First we need to get some ra2 sequence to use in CoGe Blast. Search the NCBI nucleotide database for: NM_001138446. Copy the Fasta sequence of the mRNA.
Now go to the website for CoGe: http://synteny.cnr.berkeley.edu/CoGe/ (you can just google CoGe and you’ll see it a few pages down). Click on “CoGe Blast” and paste your sequence in the “Sequences field”. It is not necessary to have a Fasta header but it helps keep track of things.
Now we need to decide which organisms we will Blast. Only (mostly) completed genome sequences are available from this window (more on how to add other sequences later on). In the “Organism Name” field search for Sorghum, Rice, Zea mays, and Brachypodium and add them in turn by hitting the “+add” button. I find that it is best to add both the pseudomolecule maize sequence as well as the sequenced BACs as shown in the picture below. Make sure you don’t accidently add the chloroplast genomes instead of the nuclear!
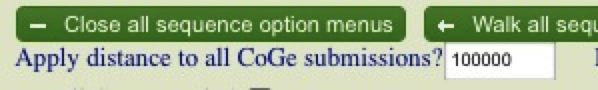
When you’re ready, hit “Run CoGe Blast” to start your analysis.
Note, this is just like Blast, only you are blasting several whole genome sequences at the same time. You can enter protein sequences, change the Blast algorithm and adjust parameters just as you would in any Blast analysis.
Your results will show both the genomic locations and a table of the “blast hits” or high scoring pairs (HSPs). The HSPs are initially ordered by organism, but you can order them by any of the criteria at the top. To sort HSPs by multiple criteria simply hit one criteria then hold shift while selecting another. I often sort by HSP# then organism. This will give you the top hits in all blasted genomes. You can evaluate the results much like any blast analysis. At this point we will pick which genomic locations to examine for gene synteny. Select the top hit from each genome.