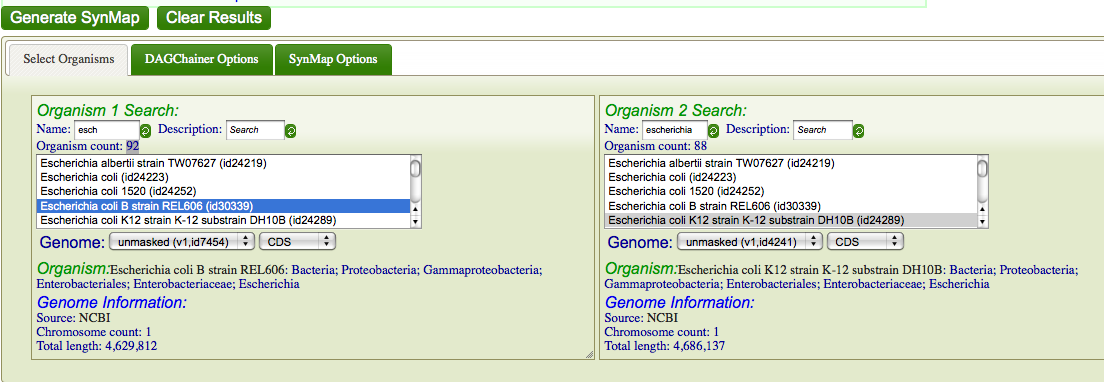
Analysis of differences found between Escherichia coli strain K12 DH10B and strain B REL606 using SynMap and GEvo analysis
In this exercise you will compare the genomes of two Escherichia coli strains, K12 DH10B and B REL606 using SynMap and GEvo analysis. In addition, we will observe the differences between these two genomes as a result of lineage divergence between the two E-coli strain and changes accumulated independently of lineage divergence. The computational tools used to do this analysis can be used for comparing genomes of any species. In two closely related bacterial genomes, for instance, several differences could be found such as transposition, insertions, deletions, duplications, inversion and translocations.
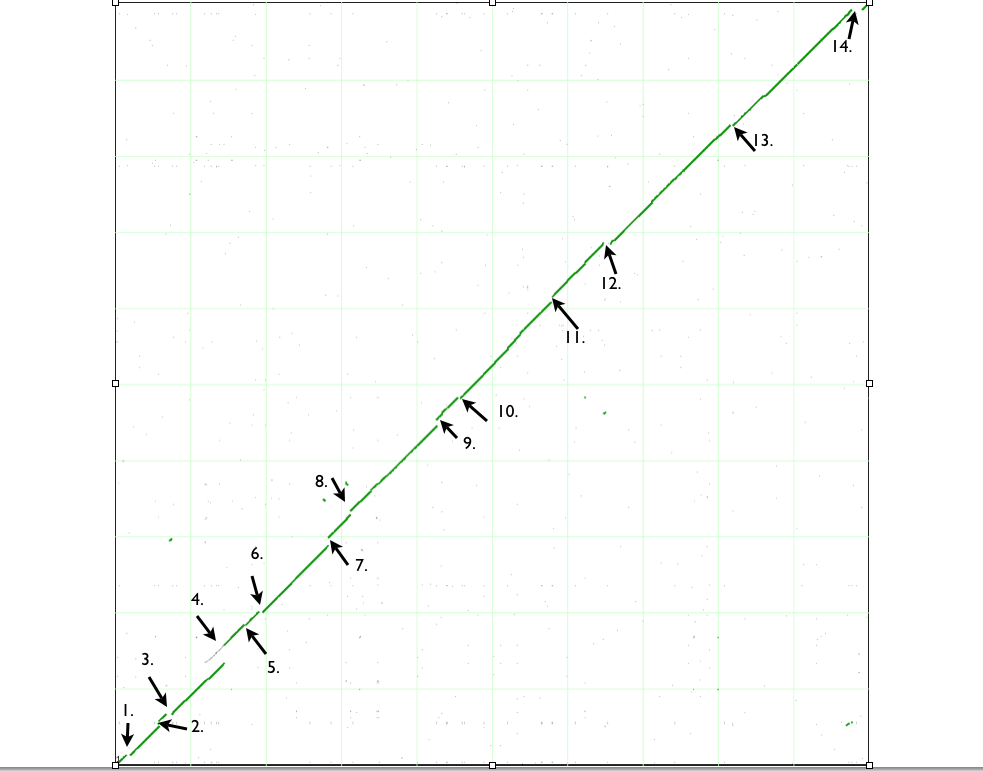
In order to accurately account for the "breaks" or discontinuties in the dotplot, we need to run GEvo analysis. GEvo uses multiple algorithms to run comparisons between the two genomic regions. These discontinuties in a dotplot represent the sites of insertions or deletions. More information on GEvo software tool can be found at: .On the dotplot diagram, use the locator to click on the green spot right before a "break". The locator will turn "red" once you have placed it on basepairs/green dots.
After clicking, a new page of GEvo (web add) will appear. Click "Run GEvo Analysis!". This will allow you to visualize and compare the genetic make-up of strain B REL606 and strain K DH10B at a given region. In this case, our region of interest corresponds to a discontunity in our dotplot.
Once GEvo analysis appears, we can begin to look for differences between the two genomes. Click on individual genes/green bars and its annotation will appear in a box.
Repeat the above mentioned steps for each discontinuity in dotplot for individual analysis. The translocation events can be observed from dotplot as well. Notice the fragments of green line all over the dotplot. Place the locator on these and run GEvo to determine which genes were translocated.
Click on the pink bars above a DNA segment and it will connect to its syntenic region. A sliding window can be used to magnify a region we want to analyze. Notice the edges of pink bars connecting syntenic regions. They may run parallel or cross each other. The latter represents an inversion event.
Evidence for deletion and insertions can be located on these genomes using GEvo. At several instants, transposon insertions will account for deletions/insertions in bacterial genomes.
You can also distinguish the segment containing different GC content relative to other parts of genomes. Under GEvo Configuration, click "Results Parameters" and select "Yes" for "Color wobble codon GC content". Click "Run GEvo Analysis!". The region containing different GC content will appear red.
Beware of the of the genes that may not seem syntenic at first. For locating the potential syntenic regions, change the sequence number on either genomes. Under GEvo Configuration, increase/decrease the number of sequences on left/right. Then click "Run GEvo Analysis!"
The DNA segments can also be aligned against each other. This is particularly helpful when locating regions of direct repeats, inverted repeats and determining percent identities between paralogs. To align multiple sequences simultaneously, click "+ Add Sequence", copy and paste the name/ID of the organism in the newly created box for additional sequences. Click "Run GEvo Analysis!". The resulting analysis will be color-coded distantly. Click on those to find syntenic regions on each sequences.