Duplicate genes created by a whole genome duplication start out with identical sets of regulatory sequence and are predicted to show identical patterns of gene expression. However, over time the expression pattern of the gene copes can diverge in different ways.
To compare the expression patterns of any homeologous gene pair in maize, download this spreadsheet and find the appropriate link.
Gene Pair Expression Patterns
Even Correlation
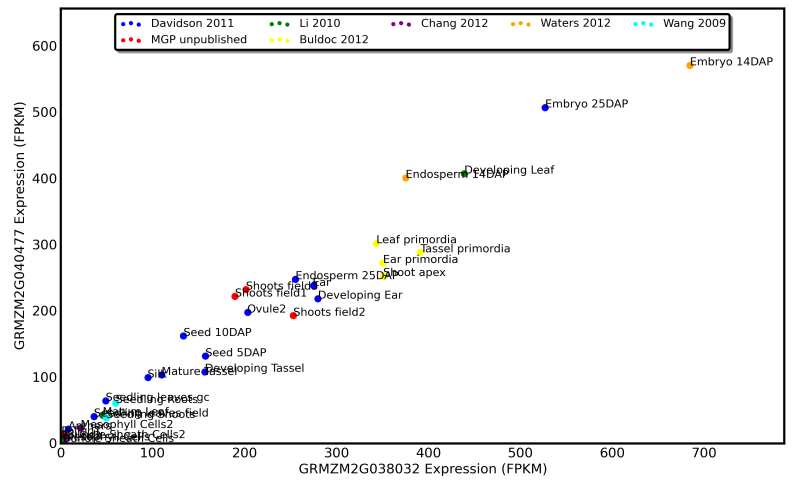
A duplicate pair of homeologous genes from maize which diverged 12 million years ago. Both genes show near identical patterns of gene expression, as well as near identical levels of expression in all tissues examined
See an up-to-date and interactive version of this graphic at qTeller
Unbalanced Correlation
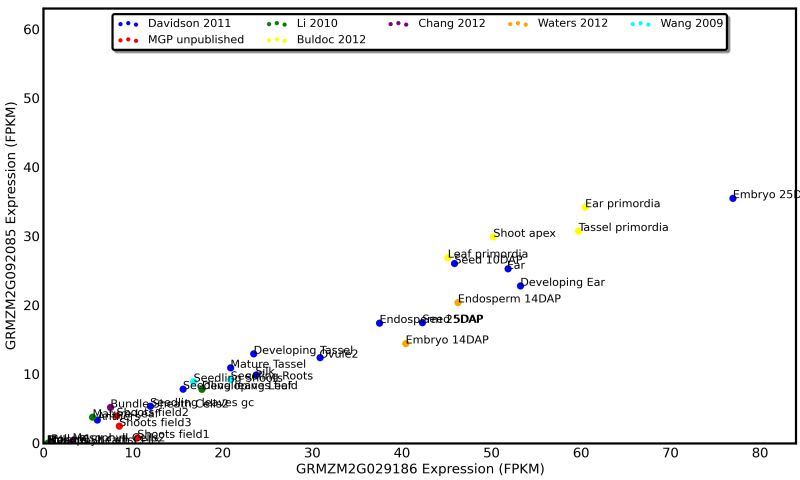
A duplicate pair of homeologous genes from maize which diverged 12 million years ago. Both genes show near identical patterns of gene expression, however GRMZM2G092085 produces only half as much RNA as GRMZM2G029186
See an up-to-date and interactive version of this graphic at qTeller
Reciprocal Expression
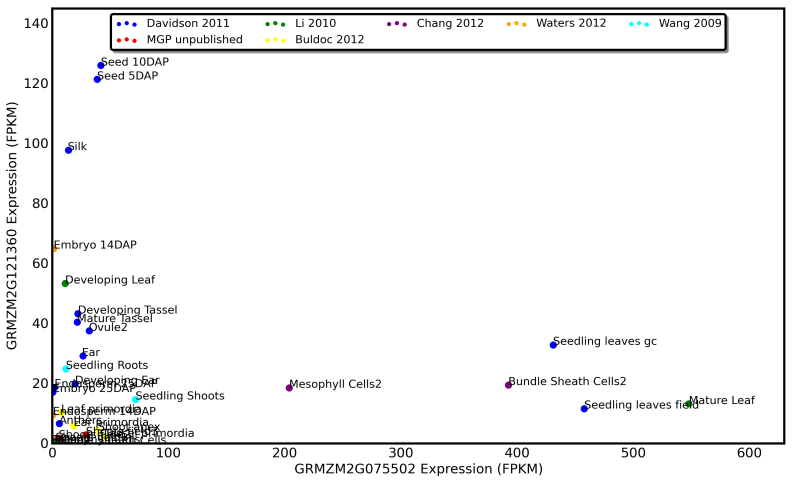
A duplicate pair of homeologous genes from maize which diverged 12 million years ago. One gene dominates expression in reproductive and embryonic tissues while the other shows high expression in mature vegetative tissues
See an up-to-date and interactive version of this graphic at qTeller
Correlated with Outliers
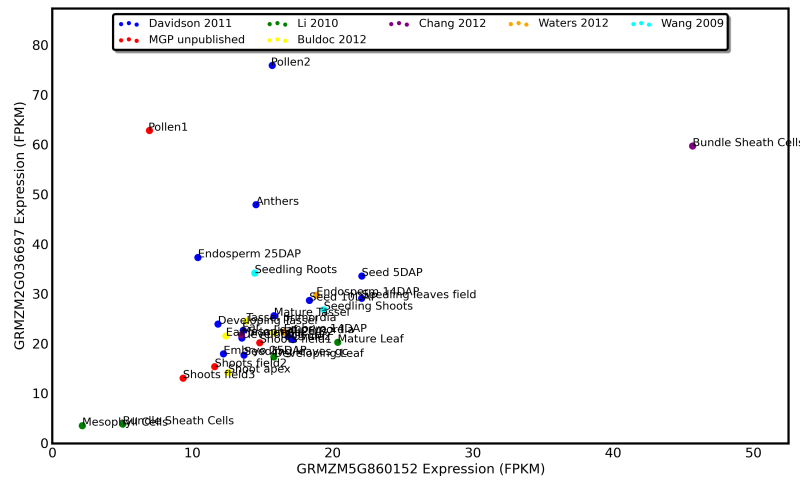
A duplicate pair of homeologous genes from maize which diverged 12 million years ago. One gene dominates expression in reproductive and embryonic tissues while the other shows high expression in mature vegetative tissues
See an up-to-date and interactive version of this graphic at qTeller
Uncorrelated Expression

A duplicate pair of homeologous genes from maize which diverged 12 million years ago. While similar tissues tend to cluster together no overall pattern can be deduced regarding the relative levels of expression for this gene pair.
See an up-to-date and interactive version of this graphic at qTeller
Potential Causes of Divergence Expression
Promoter Deletions
Natural Antisense Transcription
Transposon Insertions




