FeatView
FeatView is CoGe's tool for finding genomic features by name or description.
WARNING: It is often difficult to find a genomic feature by name. The main reason for this is the variety of names used for any given genomic feature. While CoGe can store multiple names for a given genomic feature, only the names supplied in the original data file (dataset) are used. If you are having difficulty finding a genomic feature by name, try to find the sequence for the feature and use CoGeBlast to search that sequence against the genome to which it belongs.
Contents
Quick Start
To use, just:
- Type in the name of the genomic feature in the "Name:" text box.
- Click on the "Search" button.
- Select the appropriate feature type.
- Select the appropriate genome for the feature.
- The annotation for the feature appears at the bottom of the screen.
Searching
There are several options when searching for a genomic feature. The easiest and fastest is if you know the full name of the feature and don't use any wildcards.
Searching by name
Type in the name of the feature in the "Name:" text box.
Searching by annotation
Type in the annotation of the feature in the "Annotation:" text box. By default, this search term has wildcards attached to both sides of the annotation.
Using wildcards
Wildcards can be added to either or both ends of a search term. If a wildcard is not used, then only an exact match of the search term to the entire name or annotation will happen. Otherwise, extra stuff can appear where the wildcard has been specified. For example, searching for "protease" in the annotation without wildcards will only match features associated with an annotation that is "protease" and not "metalloprotease", "protease class II", or "metalloprotease class II".
WARNING: As currently implemented in CoGe, wildcard searching is slow. Very slow. So slow it is embarrassing. If used, go for a long walk and get a cup of coffee.
Why limit a search
The more limits you place on a search, the faster it will run! Definitely recommended if wildcards are being used.
Limiting search by feature type
You can limit your search to only features of specific type (e.g. CDS or gene). The drop-down menu of feature types contains a list of all feature types currently in CoGe.
Limiting search by organism
You can search for an organism by name or description, and limit your search to only that organism. For a description of searching for organisms please see OrganismView.
Running a search
After the search criteria have been specified, just press the "Search". The results will come back and be displayed below the search criteria box. Warning: this can take a while, especially if wildcards have been used.
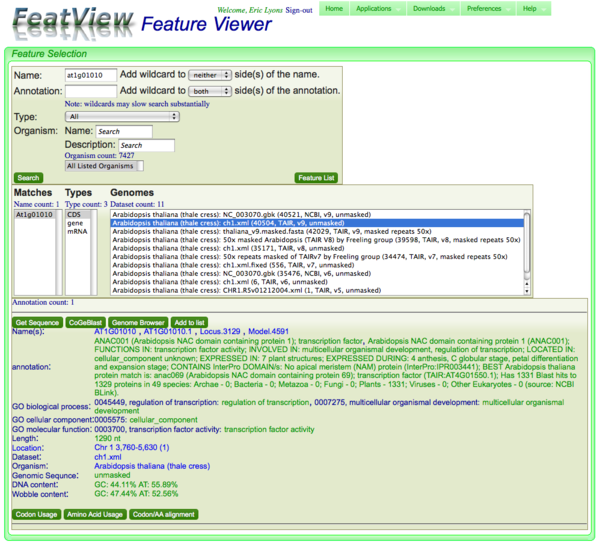
Annotation information and links for a selected genomic feature
When a feature is selected, the full annotation of the feature is displayed. This annotation box contains buttons which send the feature to other tools in CoGe, and a textual portion. The textual portion displays annotation information about the genomic feature and contains additional links.
Buttons
There are several buttons that appear with the annotation:
- Get Sequence: Launches SeqView and displays the sequence for the genomic feature in fasta format. This allows you to quickly get the sequence for the feature, add additional upstream and downstream genomic sequence to it, and translate it. The sequence can then be exported to other bioinformatics tools by cutting and pasting.
- CoGeBlast: Launches CoGeBlast, CoGe's blast tool. Which loaded, CoGeBlast will have the genomic feature's sequence loaded in the sequence submission box, ready for you to select organisms and genomes against which to blast.
- Genome Browser: Launched GenomeView, CoGe's interactive and dynamic genome browser. The genome to which the genomic feature belongs will automatically be loaded and centered on the feature.
- Add to list: This adds the feature to a feature list in FeatView. This list can be send to FeatList to display information about the features, link them to other tools in CoGe, or export their data.
CDS features only: These buttons only appear for CDS genomic features and are otherwise not displayed. They require genomic features that code for protein sequence.
- Codon Usage: Generates a codon usage table of the CDS genomic feature.
- Amino Acid Usage: Generates an amino acid usage table of the protein encoded by the CDS genomic feature.
- Codon/AA alignment: Generates an alignment of the protein sequence to the nucleotide sequence of the CDS genomic feature based on amino acid alignments to codons.
In annotation links
Information about these links can be found at the annotation information page.
Feature List
If you want to build a list of genomic features, you have the option to add features you find to a list. To display this list of features, just click the "Feature List" button located in the search criteria box. A dialog box will appear with your list of features, and you have the option of:
- Sending the list of features to FeatList which will display information about the list of features, provide links to send the list to other tools in CoGe, or export the feature's data to Microsoft Excel.
- Adding all found features to the list.
- Removing selected features from the list.
- Clearing the list of all features.
Why are there sometimes multiple annotations?
Multiple annotations are shown if there are multiple features of that type in that genome with the same name. All of these get displayed right after one another. A common case that causes this is when there are multiple splice variants of a gene, all of which share the same name